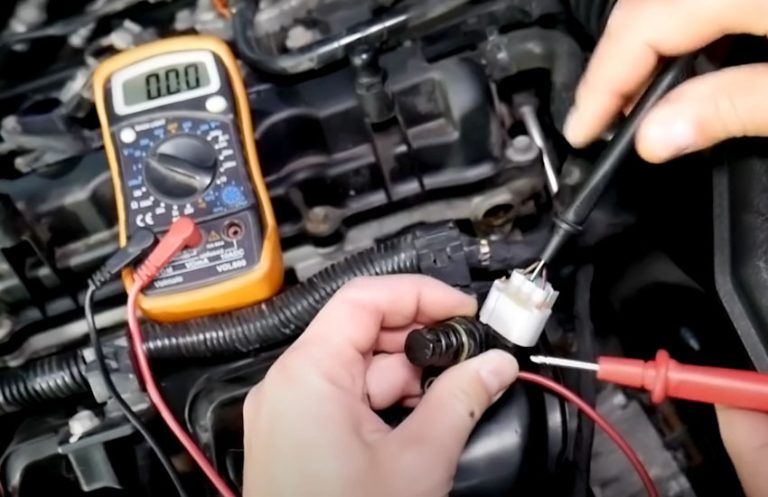
The crankshaft position sensor plays a crucial role in an engine’s ignition system, providing the engine control unit with critical information about the crankshaft’s position.
If your vehicle is experiencing problems such as rough idling, stalling, or difficulty starting, it may be necessary to test the sensor to determine if it is faulty. By conducting a resistance test using a multimeter, you can accurately assess whether the crankshaft position sensor is working as it should.
This simple procedure can help you diagnose and address any issues with your vehicle’s crankshaft position sensor swiftly, ensuring optimal engine performance and reliability.
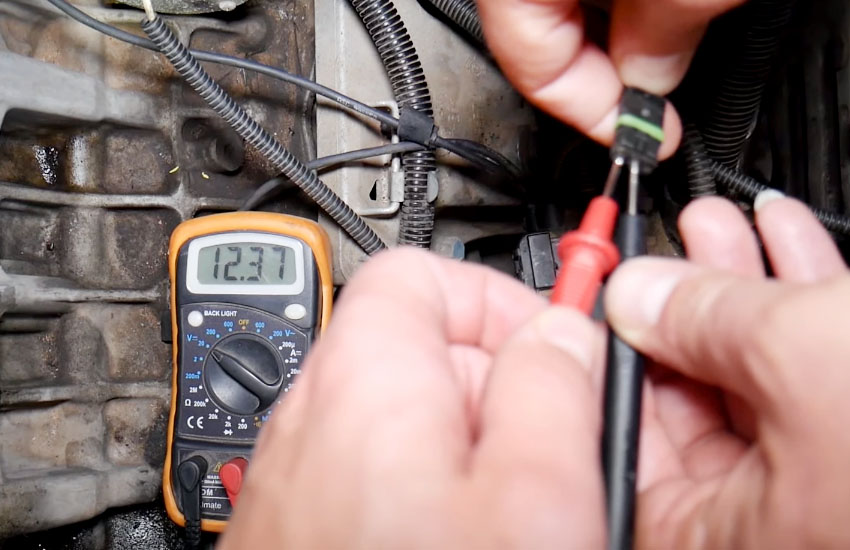

Understanding A Crankshaft Position Sensor
A crankshaft position sensor is a crucial component in modern vehicles, responsible for monitoring the position and speed of the crankshaft. This information helps the engine control module (ECM) to determine the precise timing for fuel injection and ignition. Understanding how this sensor operates is essential for ensuring the optimal performance of a vehicle.
What is a Crankshaft Position Sensor?
A crankshaft position sensor, also known as a CKP sensor, is a device that monitors the position or rotational speed of the crankshaft in an internal combustion engine. This sensor is typically located near the crankshaft at the front or rear of the engine. The CKP sensor generates a signal based on the position of the crankshaft, which is then utilized by the ECM to synchronize fuel injection and ignition timing.
Importance of Testing the Sensor
Testing the crankshaft position sensor is vital for maintaining the efficient operation of a vehicle. A faulty sensor can lead to issues such as engine misfires, stalling, and poor fuel economy. By regularly testing the sensor, car owners can identify and address potential problems before they escalate, ensuring smoother engine performance and significant cost savings in the long run.
To properly test a crankshaft position sensor, it is essential to be familiar with the specific testing procedures for a particular vehicle model. This involves using a digital multimeter to measure the sensor’s output voltage and comparing the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. Additionally, inspecting the sensor for physical damage or wear can provide valuable insights into its overall condition.
By understanding the role of the crankshaft position sensor and the importance of testing its functionality, vehicle owners can proactively maintain their cars’ performance and reliability. Regular testing of the CKP sensor can help prevent potential issues, leading to a smoother driving experience and prolonged engine longevity.
Signs Of A Faulty Crankshaft Position Sensor
A crankshaft position sensor helps in ensuring the efficient performance of an engine. However, like any other component, it can also develop faults over time. Recognizing the signs of a faulty crankshaft position sensor is crucial for maintaining the smooth operation of your vehicle. In this section, we will discuss two common signs that indicate a potential issue with the crankshaft position sensor: irregular engine stalling and difficulty starting the engine.
Irregular Engine Stalling
One of the prominent signs of a faulty crankshaft position sensor is irregular engine stalling. A properly functioning crankshaft position sensor sends vital information about the rotational speed and position of the crankshaft to the engine control unit (ECU).
This data allows the ECU to accurately calculate the timing for fuel combustion. However, when the crankshaft position sensor is malfunctioning, it may provide inaccurate or inconsistent readings to the ECU. This can lead to improper timing of the fuel injection and ignition, resulting in the engine stalling unexpectedly.
In addition to irregular stalling, you may also notice intermittent hesitations, loss of power, or rough idling when the crankshaft position sensor is faulty. These symptoms often occur during acceleration or when the engine is under load. If you experience any of these issues, it is essential to have the crankshaft position sensor tested to identify and rectify any potential problems.
Difficulty Starting The Engine
Another clear indication of a faulty crankshaft position sensor is difficulty starting the engine. The crankshaft position sensor plays a crucial role in the engine startup process.
When you turn the ignition key, the sensor detects the crankshaft’s position and sends the information to the ECU, which then triggers the fuel injection system at the precise timing for ignition.
However, if the crankshaft position sensor fails to provide accurate readings, the ECU may not receive the correct information, leading to difficulties in starting the engine.
If you find that your engine takes longer than usual to start, or it requires multiple attempts before it finally starts, it could be due to a faulty crankshaft position sensor.
This can be especially noticeable when starting the engine after it has been parked for an extended period. Ignoring this issue may lead to complete engine failure or costly repairs in the future, so it is crucial to address the problem promptly.
Preparation For Testing
Testing a crankshaft position sensor is crucial to determine if it is functioning properly. Before diving into the testing process, there are a few essential steps that need to be taken. This section will guide you through the necessary preparations to ensure a smooth and safe testing experience.
Gathering Necessary Tools
Before you begin testing the crankshaft position sensor, make sure you have the following tools on hand:
- Multimeter
- Screwdriver set
- Wrench set
- Socket set
- Safety glasses
These tools will help you access and test the sensor effectively. Having them ready will save you time and ensure a hassle-free testing process.
Ensuring Safety Measures
Testing a crankshaft position sensor involves working around moving parts and electrical systems. To ensure your safety and prevent any accidents, it is important to follow these safety measures:
- Before starting any work, make sure the engine is turned off and the key is removed from the ignition.
- Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from any debris or chemicals.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling any harmful fumes.
- Disconnect the battery to prevent any accidental shocks.
- Use caution when working around hot engine components and let them cool down if necessary.
By adhering to these safety measures, you can minimize the risk of injury and carry out the testing process with confidence.
Testing The Crankshaft Position Sensor
To test a crankshaft position sensor, start by checking its electrical connections and making sure it’s receiving power. Then, measure the sensor’s resistance and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications. Finally, inspect the sensor for physical damage or wear. If any issues are found, consider replacing the sensor for optimal engine performance.
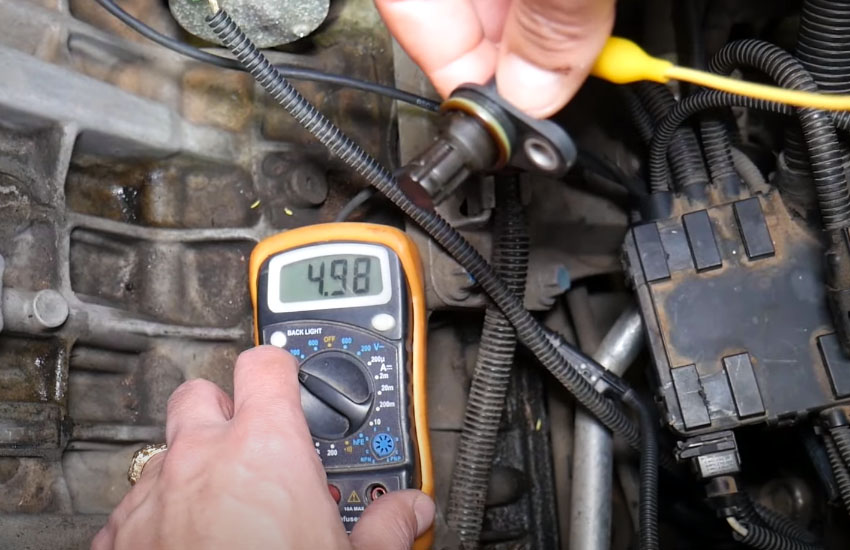

Using A Multimeter
To test the crankshaft position sensor, you can use a multimeter, which measures electrical resistance, voltage, and current. Start by locating the sensor, usually found near the crankshaft pulley or connecting rod. Disconnect the sensor’s electrical connector and set the multimeter to the resistance or ohms setting.
Connect the multimeter’s leads to the sensor’s terminals, then check the resistance reading. A healthy crankshaft position sensor will typically have a resistance value within the manufacturer’s specified range, which can be found in the vehicle’s service manual or online. This test helps determine if the sensor is functioning properly or if it needs replacement.
Inspecting For Physical Damage
Physical damage can also affect the performance of the crankshaft position sensor. Inspect the sensor for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks, frayed wires, or corrosion. Check the sensor’s wiring harness as well, ensuring there are no loose connections or exposed wires.
If you notice any damage, it’s important to replace the sensor, as physical damage can interfere with its ability to accurately detect the crankshaft’s position. This quick visual inspection can save you troubleshooting time by identifying obvious issues that may require immediate attention.
Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting test results for a crankshaft position sensor involves following a step-by-step process to ensure accurate readings. By carefully testing the sensor, you can diagnose any issues and determine if it needs to be replaced for optimal performance.
Understanding Voltage Readings
One crucial aspect of testing a crankshaft position sensor is understanding voltage readings. This test is essential as it directly indicates the health of the sensor’s electrical components. By analyzing the voltage readings, you can determine if the sensor is functioning properly or if any issues need to be addressed.
During the voltage reading test, you’ll need a multimeter to measure the voltage output from the sensor. Begin by disconnecting the sensor’s electrical connector and setting your multimeter to the voltage setting. Then, connect the positive lead of the multimeter to the positive terminal of the sensor and the negative lead to the negative terminal.
Start the engine and let it idle while observing the multimeter’s readings. In a healthy crankshaft position sensor, the voltage readings should be stable and within the manufacturer’s specified range. This ensures that the sensor is accurately detecting the crankshaft position and relaying the information to the engine control unit (ECU).
Analyzing Physical Condition
Another vital aspect of testing a crankshaft position sensor is analyzing its physical condition. This test helps determine if any visible defects or damages are present that may affect its functionality. A damaged sensor can lead to inaccurate readings or complete failure, resulting in engine performance issues.
Inspect the sensor for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or loose connections. Check the wiring harness for any frayed wires or exposed insulation. Ensure that the sensor is securely mounted and aligned properly.
While physical inspection can provide some insights, it’s essential to note that not all issues are visible. A sensor may appear to be in good condition externally but still have internal problems. Therefore, conducting additional tests, such as voltage and signal testing, is crucial to accurately assess the sensor’s overall health.
Conclusion
To conclude, testing a crankshaft position sensor is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of your vehicle’s engine. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively diagnose any issues with the sensor and address them promptly. Remember to take the necessary safety precautions and consult a professional if needed.
Proper maintenance and regular testing of the crankshaft position sensor can help prevent potential engine problems and ensure a smooth driving experience.